
What Is an HDD?
In the previous blog posts, we explained what servers and a network switches are. In this article, we will move ahead and, this time, focus on a specific type of storage equipment - HDDs.
HDDs are important for all kinds of people and organizations as they are essential storage devices for desktop computers, consumer electronics and enterprise storage arrays in data centers. In this blog post, we will first define what an HDDs is, explain its functionality and significance, and compare it to its newer alternative - an SSD.
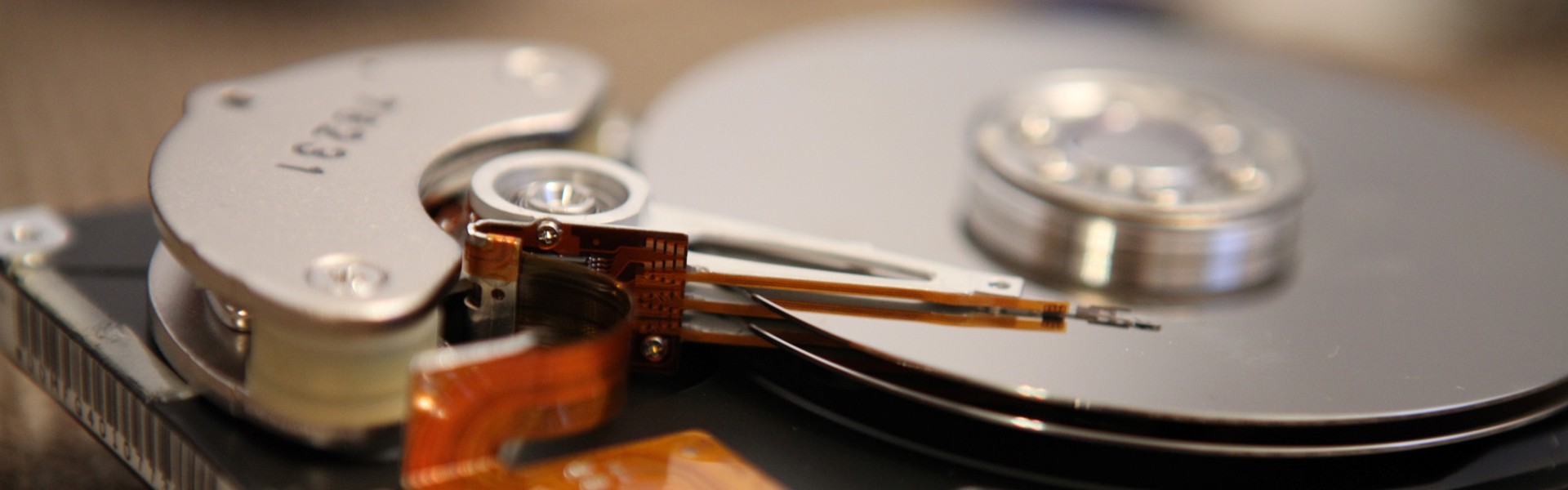
An HDD, short for a 'hard disk drive', is a type of non-volatile electromechanical data storage equipment. Non-volatile refers to a crucial characteristic of HDD: it stores data even without a power supply – when a device is turned off. Electromechanical refers to the fact that it uses one or more firm, rapidly rotating disks that are covered in a magnetic material. Besides, digital data stored on HDDs can be accessed in a random-access manner, i.e., in a way that allows storing and retrieving data in any arbitrary order.
HDDs are located in a drive bay and are linked to a motherboard through an Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA), Serial ATA, parallel ATA or Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) cable, among other formats. Each HDD also has a connection to a computer's power supply unit.
In everyday English, the hard disk drive (HDD) is often referred to as a 'hard disk', 'hard drive' or 'fixed disk'. Although in everyday English, all three expressions usually apply to the same thing, i.e., the actual data storage device, in a professional environment, the term 'hard disk' refers to the actual rotating magnetic disk inside the device.
How HDDs Work
The fundamental HDDs consist of several disks made of aluminum, glass, or ceramic, which are coated in a magnetic material. These disks are part of a sealed chamber, which also includes a spindle, a motor, and an arm with several read-and-write magnetic heads. Disks are located around a spindle and rotate with the help of a motor connected to a spindle. The read-and-write magnetic heads record data on and from the disks while the motor rotates them at up to 15,000 rotations per minute. This process can be compared to the mechanism of record players with LP vinyl records and a needle attached to an arm.
There are two essential characteristics of HDDs that affect their functionality and usage. First, the 'HDD form factor' is connected to the HDD's actual size (i.e., length, width, and height), geometry and the position of the host interface connector. The form factor of HDDs has to comply with industry standards. This ensures that HDDs are compatible with different types of computing equipment. The two most common HDD form factors for enterprise systems are 2.5-inch (small form factor – SFF) and 3.5-inch (large form factor – LFF). The inch measurement describes the approximate diameter of the rotating disk inside the sealed chamber.
Second, 'HDD storage capacity' is connected to the amount of data a specific HDD can store. The most usual HDD storage capacities are:
- 16 GB , 32 GB and 64 GB – for older and smaller devices
- 120 GB and 256 GB – for laptops and computers
- 500 GB , 1 TB and 2 TB – for storing a large number of files
- More than 2 TB – suitable for working with high-resolution files and storing large volumes of data
In their inception, HDDs were enormous devices taking up a whole room and with a capacity of only 3.75 MB . Now, they can be fitted into a desktop computer and store over 18 TB of digital data. The rapid development of new and improved technology enables the expansion of HDD storage capacity every year.

Why Are HDDs Important?
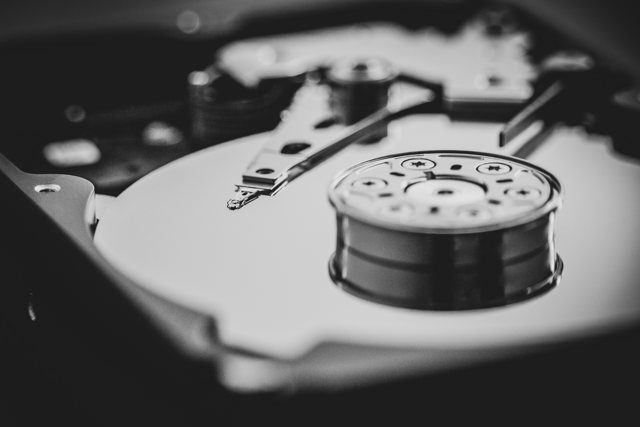
HDDs are a crucial part of any computer as they preserve data even without a power supply. They are vital for the installation of operating systems and programs as well as for saving and storing files. An HDD stores, for example, an operating system, which allows users to interact with a computer and use it. Therefore, a computer would be dysfunctional without an HDD or similar storage device.
Today, HDDs are viewed as a legacy technology. They have existed for a long time and are still widely used, especially within data centers. Industry experts predict that they will persist in the coming years or even decades as they offer certain advantages, such as a lower price and higher practicality for creating backups, in contrast to their descendants, solid-state drives (SSDs). Therefore, it is worth comparing these two types of devices as this comparison can make your future decision about which one to choose easier.
HDDs vs. SSDs – The Comparison
As already mentioned, the most significant advantage of HDDs is that they are relatively cheap. SSDs also have shorter life expectancy in terms of a restricted number of writing cycles. After that, the performance of SSDs slows down, and they fail sooner. In this respect, HDDs are more trustworthy.
On the other hand, SSDs have lower latency and faster boot times, which means they are generally faster than HDDs. That is why SSDs are used predominantly for storing data that must be accessed quickly or regularly. Besides, SSDs do not record data mechanically but use flash memory and thus include no moving parts. That is also why SSDs are generally more durable and resistant than HDDs.
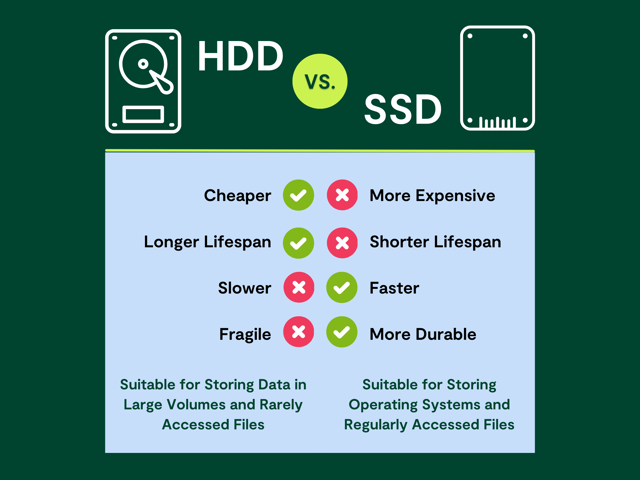
Whether to choose an HDD or SSD depends largely upon a specific user or organizational needs. In case you need to store a large amount of data or create a data backup, an HDD may be your best choice as it is affordable. If you are looking for a storage device which retrieves data fast and thus makes the frequent usage of stored data easy, SSDs might be a better alternative. SSDs, however, come with a more expensive price tag.
Besides, the selection of a suitable storage device becomes more complicated within data centers, which often comprise systems with hundreds of storage units. In such environments, the comparison of one single HDD and one single SSD is no longer valid. If you intend to purchase a large volume of units, a helpful parameter for your selection can be the price for a gigabyte on which HDDs have a lead. In fact, some SSDs may cost even eight times more than HDDs with similar storage capacity. In addition, experts predict that SSDs will be even more expensive until the 2030s, and there won't be enough of them to replace HDDs altogether as there is not enough capacity for flash memory production.
In this blog post, we explained what an HDD is, how it works and why it is essential. We have also summarized the main pros and cons of this device in comparison to its newer alternative, an SSD. Although on the performance level, SSDs are winning, HDDs still hold their place as a reliable technology with an affordable price.
At Nordic Computer, we offer mainly refurbished HDDs from different vendors, such as HITACHI, DELL/EMC, HPE, NetApp and IBM.
We also offer datacenter hardware maintenance. In case of any queries, or price requests for price or maintenance offers, do not hesitate, and contact us at sales@nordiccomputer.com or by filling out the form below.
Image Sources:
Photo by Art Wall - Kittenprint on Unsplash
Photo by Denny Müller on Unsplash