
What Is a CPU?
The world of IT hardware can sometimes be difficult to understand. There are many different components like RAM (Random Access Memory), CPU (Central Processing Unit), GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) or hard drive, which have specific functions and variations. The CPU is considered one of the most critical hardware components.
Central Processing Unit (CPU) is in everyday English often called a ‘processor’. It can be regarded as the ´brain´ of the computer because of its vast number of functions concerning input and output, processing, and storing data. It is the primary control center for all the operations occurring in a computer system.
Nowadays, you may find CPUs in smartphones, tablets, computers, data centers and even smart washing machines. Regardless of where it is placed, the CPU completes calculations using its billions of transistors. These calculations run the software, which allows the device to perform various tasks.

How Does CPU Work?
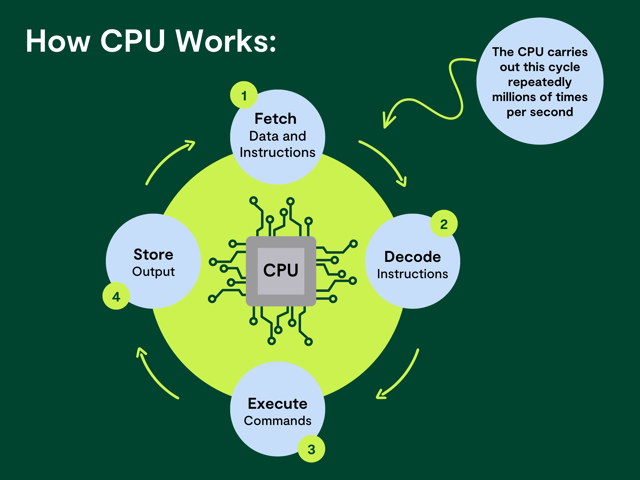
During the process of decoding data, the CPU processes the instructions it receives. While processing this data, the CPU performs the four basic steps, which are also known as the four primary functions of the CPU:
- Fetch: Every instruction has its address and is stored in memory. The processor fetches this address number from the program counter, which handles tracking of the instructions the CPU should execute next.
- Decode: In the decoding step, the programs are translated into assembly instructions to be executed. Then, the assembly code has to be decoded into binary instructions which are clear to the CPU.
- Execute: During the executing step, the CPU can do one of these things: do the calculations with its ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), transfer data from one memory to another, or jump to a different address.
- Store: After executing the instructions CPU need to give feedback, and the output data are written to the memory.
Parts of the CPU
The CPU consists of the following components:
Control Unit
The control unit supplies several functions. Firstly, it fetches, decodes and executes the instructions. The CU also issues control signals for controlling hardware, and finally, CU moves data around the system.
Arithmetic Logic Unit
The ALU has two main functions:
- Firstly, it performs arithmetic and logical operations, also called decisions. Here calculations and decisions are made.
- It acts as an access point between primary memory and secondary storage. The data are transferred between them and pass through the ALU.
Registers
Registers, a part of a computer´s memory, are used to store instructions momentarily to supply the CPU with instructions when needed. These registers hold onto the data in the form of memory addresses, and once the instruction at that location has been processed, the registers keep the memory address of the subsequent instruction. Registers come in many different varieties and serve a variety of purposes.
Cache
A cache can be described as a small amount of high-speed Random Access Memory (RAM) directly within the CPU. It temporarily holds data and instructions that might be reused by the CPU. This allows the CPU to process faster as it does not wait for data and instructions to be fetched from the RAM.
Buses
Buses are high-speed internal connections. They are used to send out data and signals between the CPU and other components. Commonly, three types of buses are used:
- Address bus – carries data bits from the processor to other components, including primary memory and input or output devices.
- Data bus – responsible for carrying data from the processor and other components
- Control bus – transferring the signals from the processor to other components and clock´s pulses as well
Clock
Each CPU holds a clock which coordinates all the computer components. This clock sends out a systematic electrical pulse resulting in compliance of all components. Clock speed is known as the frequency of these pulses and is measured in hertz. Simply put, the higher the frequency, the more instructions can be performed at any given moment.
Types of CPU
Single-Core CPU
This is one of the oldest kinds of CPU and has only one single core processing the operations – one operation at a time. Single-core CPU switches between different data streams whenever more than one program has been started. They are highly dependent on the clock speed. For that reason, this CPU is not suitable for multitasking. It might be found in today´s smartphones.
Dual-Core CPU
This CPU has two cores within a single integrated circuit. Each core has its cache and controller, which are linked together to be able to work as a single unit. Thanks to that, dual-core CPUs work faster than single-core CPUs and handle multitasking much more efficiently.
Quad-Core CPU
This CPU has a chip with four units, also known as cores which handle reading and executing CPU instructions such as cache, memory management and input/output ports. Quad-Core CPUs come with two dual-core processors within a single integrated circuit or chip.
Even though the CPU once played a significant role in terms of the speed and response of any computing device, nowadays, it is not as crucial for the overall performance of a system. However, all computing devices require some CPU; thus, the type of CPU you choose matters.
Nordic Computer has a wide range of refurbished CPUs from brands like HP, IBM, DELL EMC, INTEL, CISCO, LENOVO, and NETAPP. All our CPUs are thoroughly tested before leaving our warehouse and come with the standard 3-year warranty with the possibility to extend it.
We also offer datacenter hardware maintenance. In case of any queries, or price requests for price or maintenance offers, do not hesitate, and contact us at sales@nordiccomputer.com or by filling out the form below.
Image Sources:
Photo by Fidel Fernando on Unsplash
Photo by Christian Wiediger on Unsplash